Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of ever-evolving technologies such as solar heating, photovoltaics, solar thermal energy, solar architecture and artificial photosynthesis.
NET METERING
Net metering allows residential and commercial customers who generate their own electricity from solar power to feed electricity they do not use back into the grid. Many states have passed net metering laws. In other states, utilities may offer net metering programs voluntarily or as a result of regulatory decisions. Differences between states' legislation and implementation mean that the benefits of net metering can vary widely for solar customers in different areas of the country.
What Is Net Metering?Net metering is a billing mechanism that credits solar energy system owners for the electricity they add to the grid. For example, if a residential customer has a PV system on the home's rooftop, it may generate more electricity than the home uses during daylight hours. If the home is net-metered, the electricity meter will run backwards to provide a credit against what electricity is consumed at night or other periods where the home's electricity use exceeds the system's output. Customers are only billed for their "net" energy use. On average, only 20-40% of a solar energy system’s output ever goes into the grid. Exported solar electricity serves nearby customers’ loads.

GRID TIE SYSTEMS
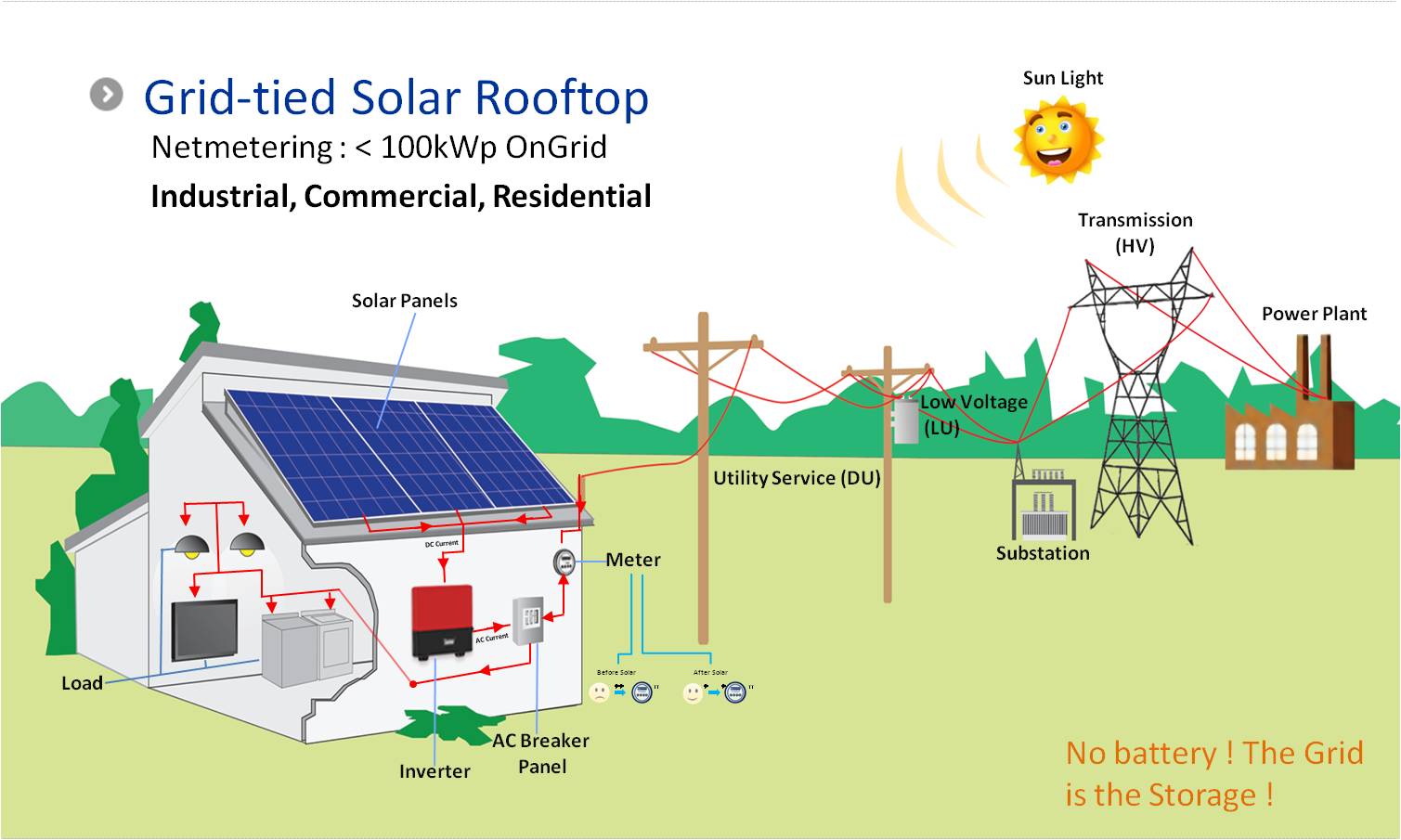
When energy is generated by the solar panels on the roof of your property, it’s sent directly to the electricity grid where it will be available for use by anyone connected to the grid.
When your property needs power, it will draw the energy for this directly from the grid. Gross metering is measured with two separate meters (one measuring the energy that is feed into the grid and the other measure the energy used by your property) so it’s easy to assess what comes in and out.
- Your solar system uses sunlight to generate electricity.
- Your gross generation meter measures all of the electricity produced by your solar system, and sends it to the electricity grid.
- Your consumption meter measures all the electricity that you’ve consumed in your home.
The Gross Metering for domestic consumers is to “…incentivize domestic consumers to install rooftop solar plants because of higher and faster returns on their investments.” We will help you in explaining how Gross Metering is a better option than the other one. First let us have a look at the KERC prices for domestic consumers:
Consider, a domestic consumer have put up a 10 kW rooftop solar PV system without getting capital subsidy. A 10 kW system will generate ~1200 units a month. Assuming the resident consumes only 200 units, the monthly bill that the client will get from DISCOM is INR 988 (leaving fixed charges) as per the tariff in the above table.
Now let us analyze both the metering options. If it is a Net-Metering, one will export the excess solar power back to the grid after self-consumption. Here the client will export back the excess 1000 units for which he/she will earn INR 7080 (i.e. 1000 units x INR 7.08 per unit). This will also zero out the energy bills for the client.
On the other side, if it is a Gross-Metering option, the client will export all the solar power back to the grid without any self-consumption, for which DISCOM will pay INR 7.08 and the client will get INR 8496, plus he will be paying INR 988 for the 200 units that he/she will consume from DISCOM. Hence the net savings for the client is INR 7508 (after deducting INR 988 from the earnings from Gross-Metering). So the earnings from rooftop solar PV system is increased by INR 428 per month and INR 5136 per year accordingly with Gross-Metering mechanism.
In the similar fashion, below table shows you the earning calculation considering different consumption patterns from 200 units to 1200 units per month by the domestic consumer:
From the above calculations we can say that, as the client’s consumption is increasing, the earnings from the solar PV system is on the decreasing trend and will reach zero if the client’s consumption is 1200 units per month in Net-Metering. Where as in Gross-Metering the earnings will be INR 608 per month even if the consumption is 1200 units a month.
- Earnings from Gross Metering is more profitable than Net metering
- Earnings from the solar PV system is inversely proportional to grid power consumption. Lesser the grid consumption, higher is the earning and the same will increase to some more extent in Gross-Metering.
- A consumer with same units consumption as that of solar generation will still make INR 7296 per year in case of Gross-Metering.
- The ROI for domestic rooftop solar PV systems will be reduced considerably in Gross-Metering compared to that of with Net-Metering.
OFF-GRID SYSTEMS
Off grid systems supply electricity to properties that are not connected to, or have chosen to reduce the electricity usage from the grid. These systems are often referred to as stand-alone power systems or remote area power systems, these systems are independent power stations capable of powering a wide range of applications with dependable and reliable electricity that is no different to that supplied by the electricity grid. Whether it is for a small or large new or existing home, a station, business or an entire community that depends on large diesel generators, off-grid stand alone power systems are commonly the reliable, clean, hassle free, cost competitive answer!
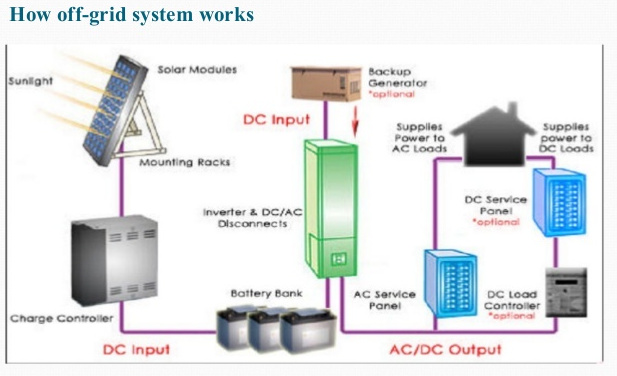
Simply sun shines on solar PV panels on your roof or mounted near your house. These panels generate electricity which is used to power your home and charge your batteries. The batteries allow you to store electricity for use at night or times of low production like cloudy days.
- Solar PV panels mounted on your roof or near your house capture energy from the sun and convert this energy into DC electricity
- A Solar Inverter converts this DC electricity into 230V AC electricity.
- The main switchboard takes electricity from the solar inverter or battery inverter and sends it to power your home.
- The battery inverter is two way and can take surplus electricity from the main switchboard and convert in into DC electricity to be stored in batteries or demand is their convert stored DC electricity from the batteries into AC electricity to power your house.
Off-grid solar electricity is complex and getting it wrong leads to expensive mistakes. What follows below is a simplified explanation for understanding how an off-grid solar power system works and the process we go through to design your system correctly.
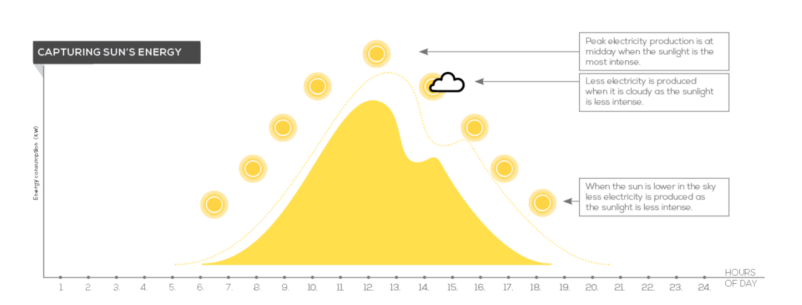
The more intense the sunlight that shines on your solar PV panels the more electricity that is produced, so when the sun is low in the sky less electricity is produced. Likewise on cloudy days and overcast days, less electricity is produced than on a bright sunny day. In the winter less electrical energy is produced than during the summer as the sun shines for less hours. the dotted line represents the increased electricity production on a summers day.
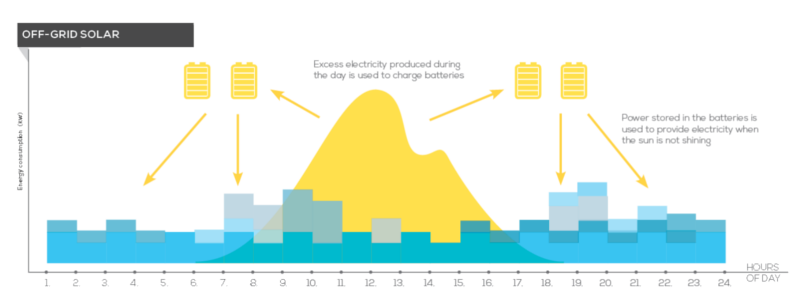
In the diagram above you can see how surplus electricity produced during the day is used to charge batteries which in turn produce electricity to run the house in the evening. As a general rule we design our systems to have enough battery storage so a household can last without significant sunshine for 2-3 days.
HYBRID INVERTER SYSTEM
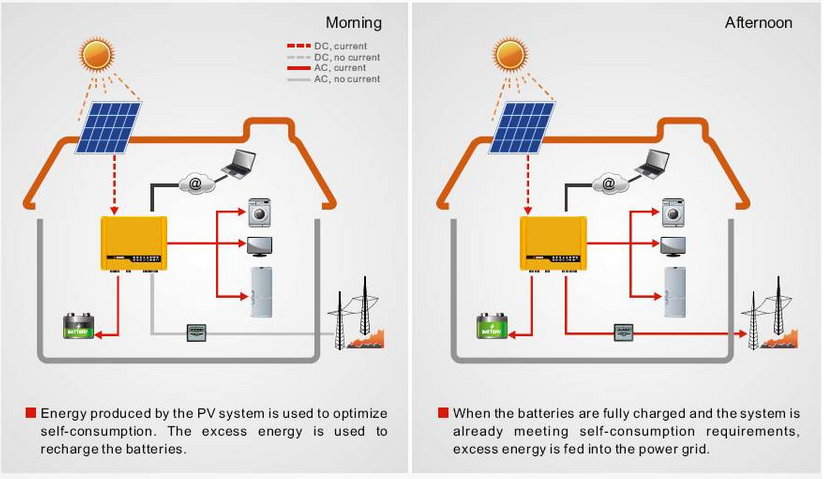
An intelligent hybrid inverter or smart grid inverter is a new generation of dedicated uninterruptible power supply (UPS) applications using renewable energy for home consumption, especially for solar photovoltaic installations.
How it works
- Step-1: It works as both the off-grid and on-grid systems – during the day when the sun is shining brightly, the panels convert the rays to electricity and any excess will be stored in the batteries, much like the off-grid systems. However, if even after storing in batteries and using electricity in your home, there is still excess power, the system then sends this excess back to the grid according to the rate of the chosen feed in tariff, similar to the on-grid system.
- Step-2: Since the batteries are continually charged during the day, they are able to store enough energy. During times of outages and little or no sunshine, the home can draw its power from these batteries. If however, these adverse situations last for too long, the batteries can be recharged from the grid and your home will only use as much power from the grid as is required to recharge the batteries.
- Step-3: Till the batteries are recharged or the grid begins to function as usual, your home will still have an uninterrupted power supply since it will draw power from the grid. This keeps the cost of power down.
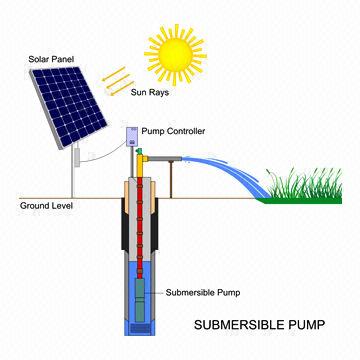
SOLAR IRRIGATION PUMP
A solar powered pump is a pump running on the power of the sun. It makes efficient use of solar energy and converts it into electrical energy for pumping water to great heights. A solar powered pump can be very environmentally friendly and economical in its operation. This system operates on power generated using solar PV (photovoltaic) system. The photovoltaic array converts the solar energy into electricity, which is used for running the motor pump set. The pumping system draws water from the open well, bore well, pond etc. The water pumping system can be used to irrigate land, when the water is to be pumped from a depth of well or a pond. The solar water systems can be designed based on the requirement of high water volume or low water volume pumping.
There are two types of solar water pumps- For high lifts and low volumes: Helical Rotor pumps are used
- For high volumes and low lifts: Multistage centrifugal pumps are used.
- It helps in saving Energy.
- There is no fuel cost - as it uses available free sun light.
- No electricity required.
- Can be operated lifelong.
- It is highly reliable and durable.
- Easy to operate and maintain
- It is also useful for clean, drinking water sanitation and also irrigation.
SOLAR STREET LIGHTS
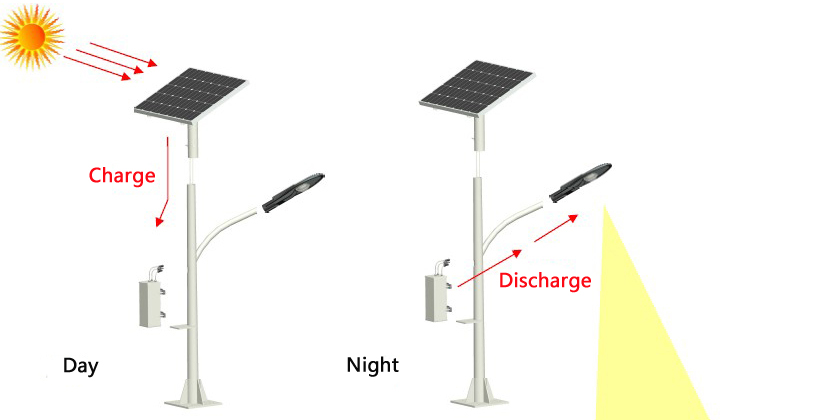
Solar-powered lighting consists of a solar panel or photovoltaic cell that collects the sun's energy during the day and stores it in a rechargeable gel cell battery.
The intelligent controller senses when there is no longer any energy from the sun and automatically turns the LED light on using a portion of the stored energy in the rechargeable battery.
SOLARIZER ELITE - HYBRID SOLAR HOT WATER SYSTEM
Conventional Solar hot water systems will deliver hot water only when the sun is shining. however during the days of monsoon and overcast days. its necessary to use electrical back up heater built in the solar tank to heat the water. Electrical heaters consume precious and expensive electrical energy.
The storage tank in the conventional solar water heater is designed to provide bulk hot water for consumption during non-sunshine hours and this restricts the withdrawal of hot water as per your convenience.
For Example, if you would like to bath or use hot water during the mid-day when the sun radiation is at peak, the cold water equal to the volume of the hot water withdrawn cannot be reheated as the remaining sun shine hours is not adequate to provide energy. Hence there will be no hot water for consumption next day, Unless auxilary electrical heating is used.
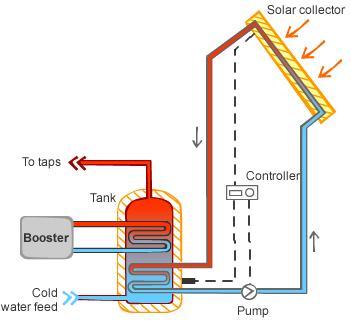
A solarizer Elite - Hybrid solar hot system consist of a large solar tank connected by pipes to solar collectors which are mounted on terrece of your house and to a heat pump. The heating of the water in solar tank is done by the solar collector as well as the heat pump. The heating sequence and logic controlled by a very sophisticated electronic controller that automatically ddecides on how to share the heating water.
The diagram explains how solar collectors and heat pumps work together and heat up the water in the storage tank shown in the diagram is a twin coil for the solar heating source and secondary heating source (In this case heat pump). The system hhas an automated control ststem to switch on and off of the heat pump(s). depending on the heat load of the building. EMMVEE also manufactures enameled tanks for the large volume of the storage with and without single and twin helical coil heat exchanger.
Corrosion resistant and hygiene Glass enamel coated tank Anti-freezing and efficient heating Glycol-water based heat transfer fluid Efficient heat transfer Helical coil heat exchanger (for solar and heat pump circuit) Heat pump Air source Low power consumption High efficient circular pump Automated operation Sophisticated electronic controller for solar circuit and heat pump Design FLexibility Easy cascading for higher volume of water Easy Monitoring Heat metering facility (optional) Remote monitoring via internet (optional) European quality solar collector Solar key mark certified solar collectors Wide range Available in 500, 1000, 2000 and 3000 liter storage capacity Applications Homes, Hospitals, Hotels and Hostels


